How Do Many Sociologists Explain Gender Inequality in Society
Here are 8 primary causes of gender discrimination. Sociologists within this subfield study a wide range of topics with a variety of research.

Conceptualising Gender Equality In Relationships Revisesociology
A by noting that women are physically weaker than men B.

. In this light changing institutions such as the ascendance of shareholder-centered corporate governance model finance-friendly policies since the late 70s credentialism and deunionization all contribute to. Many societies try to address the class issue but with little success. Societies such as Britain is the relationship between social class and gender-based forms of stratification.
Gender inequality is experienced differently across cultures. The sociology of gender is one of the largest subfields within sociology and features theory and research that critically interrogates the social construction of gender how gender interacts with other social forces in society and how gender relates to social structure overall. Alternatively if those actions became rare and were not replaced by alternative actions with similar effects then either the degree of gender inequality experienced by some people would decline or the persistence of gender.
Tap card to see definition. Sociologists examine the structural conditions of social inequality. Sociologists have formulated theories to explain the existence of social inequality in human relations.
Social economical classes are the most common in most societies and have attracted attention from many sociologists. One institution in which gender inequality remains extremely resistant to change is the family where it is not only a matter of social relations at the individual family level but also a political matter involving questions of power and hierarchy in the larger society. We start with gender inequality in income and.
Radical feminism suggests that society should be matriarchal this would continue the process of gender inequality but just the other way round. By noting that women are less aggressive than men C. Many societies try to address the class issue but with little success.
Lets look at examples of such inequality much of it taking the form of institutional discrimination which as we saw in Chapter 7 Deviance Crime and Social Control can occur even if it is not intended to happen. Stanford University sociologist Shelley Correll and her colleagues research on the motherhood penalty found that. Economic gender and race to name a few.
Social economical classes are the most common in most societies and have attracted attention from many sociologists. Mothers are less likely to be hired than. Durkheim 19331997 described a social world in which roles functioned to support a society.
We have said that the womens movement changed American life in many ways but that gender inequality persists. Also Know what causes gender inequality. Click card to see definition.
In pre-capitalist societies the class dimension is relatively insignificant and in many such societies when can view gender as one of the primary forms of social stratification that is. We start with gender inequality in income and. Feminist sociologists argue that many of the above changes have been brought about by their attempts to highlight gender inequalities in society and their efforts to encourage the government schools and teachers to actually combat patriarchy and provide genuine equality of opportunity which has lead to raising the expectations and self-esteem.
How do many sociologists explain wonder inequality in society i in society. The right for well-paid work proper medical care education and creating a family at the right age. In modern societies inequality manifests in social and economic classes power income access to health facilities academic gender and other forms.
Social inequality is not about individual inequalities but about systematic inequalities based on group membership class gender ethnicity and other variables that structure access to rewards and status. An artificial boundary that allows women to see the next occupational or salary level even as structural obstacles keep them from reaching it is called the glass escalator. To say that actions reinforce gender inequality means that they either bolster the stability of gender inequality or help to make it more severe.
Explanations for gender inequality include. Another limitation of radical feminism is that instead of promoting marriage it does the opposite that women should be rid of all these stereotypical roles this in a way promotes promiscuity and even unhealthy relationships. By noting that women alone can give birth to and nurse intan D.
In modern societies inequality manifests in social and economic classes power income access to health facilities academic gender and other forms. Gender relations are the result of the way. The central thesis of sociological accounts of gender relations is that these biological facts by themselves do not determine the specific form that social relations between men and women take.
By noting that women tend to have little interest in business pursus ited States. Most sociologists believe that formal and informal institutions are more critical in explaining the rising inequality observed in advanced economies. Mothers are less likely to be hired than childless women who have the same work experience and qualifications and mothers are offered significantly lower starting pay than equally qualified childless women for the same job.
There are differences in individuals abilities and talents. Lets look at examples of such inequality much of it taking the form of institutional discrimination which as we saw in Chapter 7 Deviance Crime and Social Control can occur even if it is not intended to happen. Arguments against this view is possibly LGTBIQ community despite most people being socialised into traditional gender norms many people today develop LGTBIQ identities.
There are factors which directly influence the opportunities of women and men in society. It as if people are just pretending to obey social norms but when you dig deeper and look at things more qualitatively this isnt necessarily the case and everyone is doing their own thing and it. Today social media plays a large role in social reform campaigns and was harnessed in 2014 by British actress Emma Watson on behalf of the United Nations to launch a campaign for gender.
In 2011 a report by the Resolution Foundation found that women were 40 less likely to improve their social status than men. This does not imply however an even stronger view that gender relations have nothing to do with biology. On one end of the spectrum lies a conservative perspective that sees inequality as a utility in maintaining the status quo of society.
We have said that the womens movement changed American life in many ways but that gender inequality persists. Sociologists study how these social reforms help shape or change social inequality that exists in a society as well as their origins impact and long-term effects. Gender inequality permeates society at all levels and in the context of most if not all social institutions.
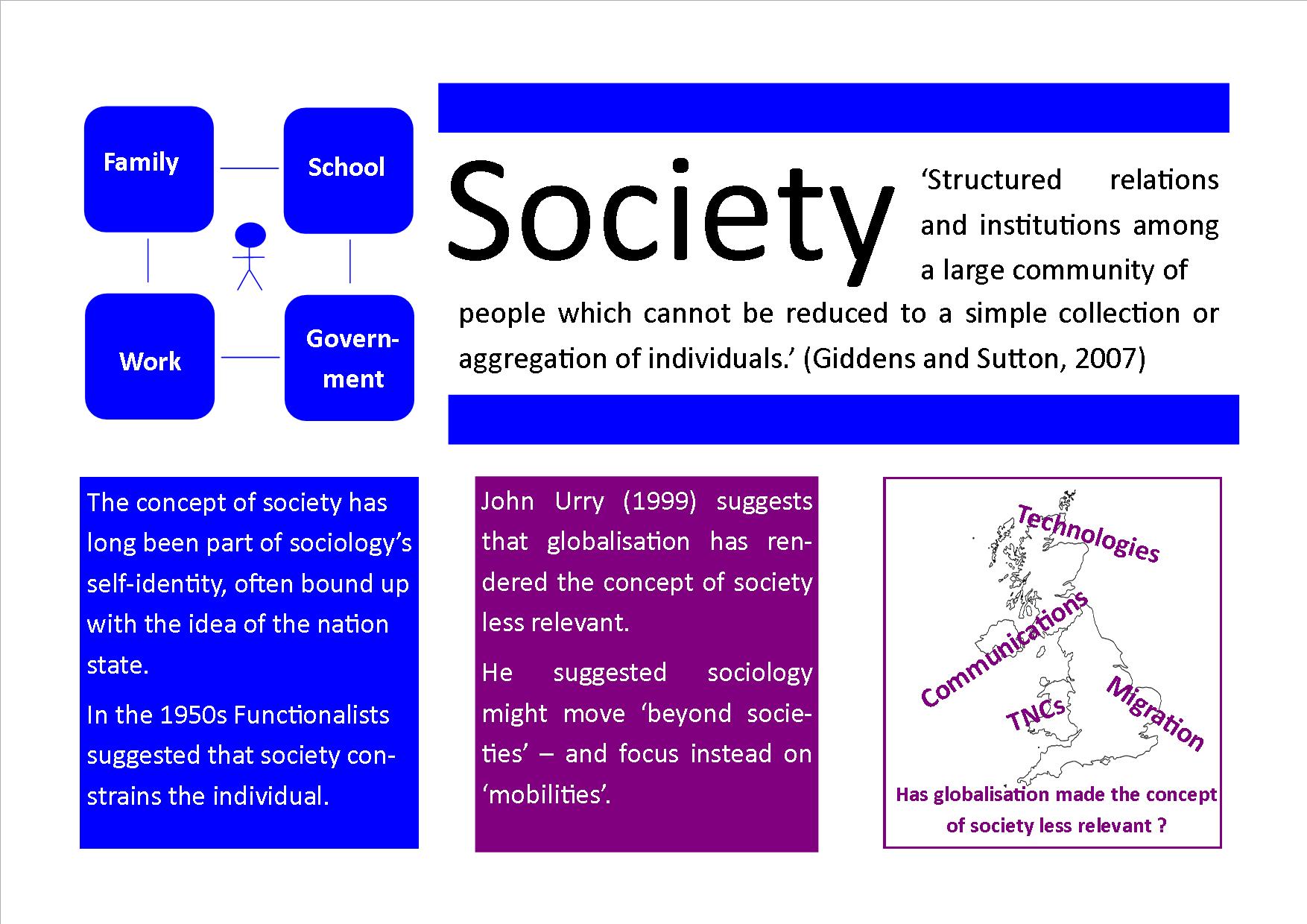
What Is Society And Should Sociologists Study It Revisesociology

Feminist Theory A Summary For A Level Sociology Revisesociology

0 Response to "How Do Many Sociologists Explain Gender Inequality in Society"
Post a Comment